Social Mobility
What is Social Mobility?
The relationship between a person’s background and starting point in life and their future occupation, income and wealth achieved as adults.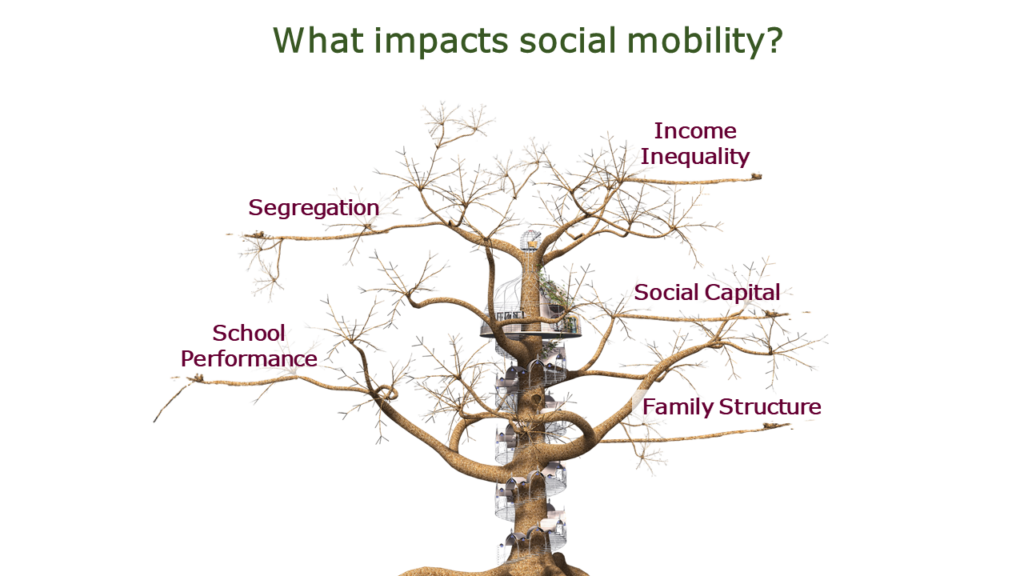
What impacts social mobility?
- Segregation
- Income Inequality
- School Performance
- Social Capital
- Family Structure
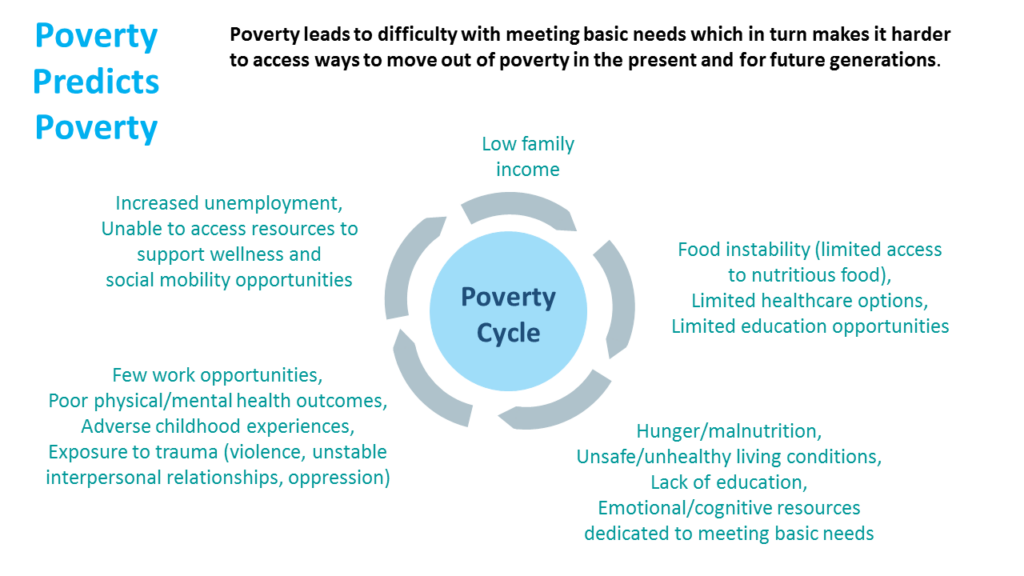
Poverty Predicts Poverty
Poverty leads to difficulty with meeting basic needs which in turn makes it harder to access ways to move out of poverty in the present and for future generations.
- Increased unemployment, Unable to access resources to support wellness and social mobility opportunities
- Low Family Income
- Food instability (limited access to nutritious food), Limited healthcare options, Limited education opportunities
- Hunger/malnutrition, Unsafe/unhealthy living conditions, Lack of education, Emotional/cognitive resources dedicated to meeting basic needs
- Few work opportunities, Poor physical/mental health outcomes, Adverse childhood experiences, Exposure to trauma (violence, unstable interpersonal relationships, oppression)

What do communities need?
Opportunity
- Accessible Employment Providing Living Wage
- Financial Well-being
- Safe, Affordable Neighborhoods/Housing
- Mental/Physical Wellness
- Healthy Families
- Accessible High Quality Schools/Childcare
The Opportunity Atlas
Does the neighborhood you grow up in impact how much you earn as an adult? The Opportunity Atlas provides an interactive visual of outcomes by census-tract. Learning more about the barriers to social mobility can drive the development of local solutions. Learn more about the Opportunity Atlas here.